Bayt Mahsir
Bayt Mahsir
بيت محسير | |
|---|---|
 Panorama from west, 2008 | |
| Etymology: The house of Mahsîr[1] | |
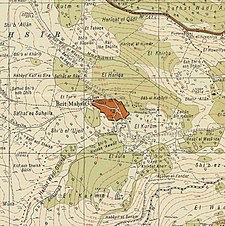
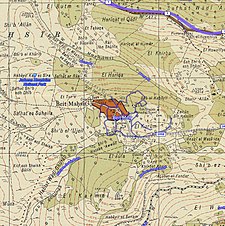
A series of historical maps of the area around Bayt Mahsir (click the buttons) | |
Location within Mandatory Palestine | |
| Coordinates: 31°47′40″N 35°02′05″E / 31.79444°N 35.03472°E | |
| Palestine grid | 153/133 |
| Geopolitical entity | Mandatory Palestine |
| Subdistrict | Jerusalem |
| Date of depopulation | May 10–11, 1948[4] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 16,268 dunams (16.268 km2 or 6.281 sq mi) |
| Population (1945) | |
| • Total | 2,400[2][3] |
| Cause(s) of depopulation | Military assault by Yishuv forces |
| Current Localities | Beit Meir,[5][6] Mesilat Zion[6] |
Bayt Mahsir (Arabic: بيت محسير) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Jerusalem Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on May 10, 1948, by the Harel Brigade of Operation Makkabi. It was located 9 km west of Jerusalem.
History[edit]
A large medieval oil press, about 10 x 35 meters, was recorded NW of the village in 1947 by representatives from the Palestine Antiquities Department. The representative thought it was from the Ayyubid or Crusader era, later examination of surviving pictures by D. Pringle determined them to be from the Crusader era. It has since been destroyed.[7][8]
Ottoman era[edit]
In 1838 Beit Mahsir is noted as a Muslim village, located in the District of Beni Malik, west of Jerusalem.[9] An Ottoman village list from about 1870 found 50 houses and a population of 130, though that population count included men only.[10][11] In 1883, the PEF's Survey of Western Palestine (SWP) described Beit Mahsir as "a village of moderate size, standing on a hill at the end of the higher spurs overlooking the lower hills on the west. It has olives to the north and a spring to the north-east."[12] In 1892, P. Baldensperger recounted a story about the 'Ajami of Beit Mahsir, "whose lands were mixed with the village lands, [he] killed several animals which were on his lands. The people thought it was enemies who did it, and one evening they hid themselves, and saw the rider, [..] He asked them what they wanted, and they told him: 'If thou art the 'Ajami, show us thy lands.' The next morning he had shown them by a boundary line all around his lands, and since then, nobody interferes with his grounds. A camel which was feeding on an olive tree was found hanged between its branches; and at another time a jackal was found standing dead with a candle in its mouth at the door of the Makam. Thus the 'Ajami punishes man and beast for going on, or taking anything from his grounds."[13] Baldensperger later recounted the meeting with a Dervish who had stayed "with 'Ajami" (apparently a mythical creature) at the 'Ajami shrine above Bayt Mahsir.[14] In 1896 the population of Bet Mahsir was estimated to be about 258 persons.[15]
British Mandate era[edit]
In the 1922 census of Palestine, during the early British Mandate of Palestine period, there were 1,367 villagers, all Muslims,[16] increasing in the 1931 census to 1,920 Muslims, in 445 houses.[17] In the 1944–45 statistics, the village had a population of 2,400 Muslims,[2] and the total land area was 16,268 dunams.[3] Of this, 1,348 dunums were irrigated or used for orchards, 6,225 dunams were for cereals,[18] while 77 dunams were built-up (urban) Arab land.[19] Bayt Mahsir had three schools; two schools for boys and an elementary school for girls. Bayt Mahsir contains a number of khirbat, including al-Huwaytiyya, al-Masi, Khatula and al-Sallam.[20] The villagers took pride in the fact that the last imam of its mosque, Shaykh Khalil As'ad, was a graduate of Al-Azhar University in Cairo.[20]
-
Bayt Mahsir 1943 1:20,000
-
Bayt Mahsir 1945 1:250,000
-
Bayt Mahsir May 10, 1948
1948 and aftermath[edit]


Already on April 12, 1948, while Bayt Mahsir was still in Palestinian hands, the Yishuv leadership made plans to populate it with Yishuv.[21] During the April–May fighting in the Jerusalem Corridor (operations 'Nachshon', 'Harel', 'Yevusi' and 'Maccabi'), Palmach units more or less systematically levelled Qastal, Qalunya and Khulda, and largely or partly destroyed the villages of Beit Surik, Biddu, Shuafat, Beit Iksa, Bayt Mahsir and Sheikh Jarrah.[22] Bayt Mahsir was depopulated on May 10–May 11, 1948, after a military assault by Yishuv forces.[4][23][24][25] Two days later, on May 13, Israeli troops contaminated the village wells with a biological warfare agent consisting of typhus and diphtheria bacteria, as part of a programme to render Palestinian resettlement impossible and ensure 'the destruction of its ability to constitute an economic and military base for enemy forces surrounding the road.'[26] In August 1948, the new Israeli leadership started finalising plans for resettling Bayt Mahsir land.[27] [28]
In 1992 Palestinian historian Walid Khalidi noted that some houses from Bayt Mahsir were still standing in the moshav of Beit Meir, identifying two large homes built of limestone that were larger than those built after 1948. He also noted that "The remains of a flour mill, a metal machine with flywheels fitted over a stone structure, can still be seen. There is a wild forest of old trees on the eastern edge of the village site, on top of the mountain. The tomb of al-'Ajami, together with other graves, are among the trees."[6] The Maqam al-'Ajami, or 'tomb of al-'Ajami', was examined by Andrew Petersen in 1994. It is located southeast of the village site, on a hill in the present Hamasrek Nature Reserve. The name is identified by Tawfiq Canaan as coming from Ahmad al-'Ajami, called the Persian, though Canaan doubted that he was of Persian origin.[29][30] The representative from the Palestine Antiquities Department dated it to the 17th century in 1947, a date which Petersen found "not inconsistent" with the architecture of the building.[31] Two books have been published about Bayt Mahsir, one in 1988, and one in 2002.[32]
Gallery[edit]
-
Bayt Mahsir, taken by the Harel Brigade 8–11 May 1948
-
Harel Brigade 81mm mortar team bombarding Bayt Mahsir, 1948
-
Members of Harel Brigade occupying Bayt Mahsir, Operation Maccabi, 1948
-
Bayt Mahsir - after the occupation, Operation Maccabi, 1948
-
Bayt Mahsir being demolished by the Harel Brigade 1948
-
The current natural landscape of the area
-
Many Sabra Cactus plants are now grown currently in this location
References[edit]
- ^ Palmer, 1881, p. 286
- ^ a b Department of Statistics, 1945, p. 24
- ^ a b Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 56
- ^ a b Morris, 2004, p. xx, village #336. Also gives cause of depopulation.
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. xxi, settlement #28.
- ^ a b c Khalidi, 1992, p. 277.
- ^ Pringle, 1997, p. 28
- ^ Petersen, 2002, p. 124
- ^ Robinson and Smith, 1841, vol 3, Appendix 2, p. 123
- ^ Socin, 1879, p. 146
- ^ Hartmann, 1883, p. 140 also noted 50 houses
- ^ Conder and Kitchener, 1883, SWP III, p. 16
- ^ Baldensperger, 1893, p. 219
- ^ Baldensperger, 1913, pp. 76-96
- ^ Schick, 1896, p. 125
- ^ Barron, 1923, p. 15
- ^ Mills, 1932, p. 38
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 101
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 151
- ^ a b Khalidi, 1992, p. 276
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 371, note #168, p. 405
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 345, note # 21, p. 396
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 233
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 235, note # 547, p. 293
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 237, note #552, p. 294
- ^ Benny Morris, Benjamin Z. Kedar, ‘Cast thy bread’: Israeli biological warfare during the 1948 War Middle Eastern Studies 19 September 2022, pages =1-25 p.7.
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 376, notes #202, 203 p. 407
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 380
- ^ Canaan, 1927, p. 251, cited in Petersen, 2002, p. 125
- ^ meaning "The Persian Sheikh", according to Palmer, 1881, p. 327
- ^ Petersen, 2002, p. 125
- ^ Davis, 2011, pp. 1, 30
Bibliography[edit]
- Al-Mahsiri, ‘Ali Islim (2002). Bayt Mahsir wa madinatuha al-Quds [Bayt Mahsir village and its city, Jerusalem]. Amman, Jordan: Dar al-Baraka lil-Nashr wal-Tawzi‘.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Baldensperger, Philip J. (1893). "Peasant folklore of Palestine". Quarterly Statement - Palestine Exploration Fund. 25 (3): 203–219. doi:10.1179/peq.1893.25.3.203.
- Baldensperger, Philip J. (1913). The Immovable East: Studies of the People and Customs of Palestine. Boston.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Barron, J.B., ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine.
- Canaan, T. (1927). Mohammedan Saints and Sanctuaries in Palestine. London: Luzac & Co. Archived from the original on 2019-05-16. Retrieved 2016-11-29.
- Clermont-Ganneau, C.S. (1896). [ARP] Archaeological Researches in Palestine 1873-1874, translated from the French by J. McFarlane. Vol. 2. London: Palestine Exploration Fund. (p. 63)
- Conder, C.R.; Kitchener, H.H. (1883). The Survey of Western Palestine: Memoirs of the Topography, Orography, Hydrography, and Archaeology. Vol. 3. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Davis, Rochelle A. (2011). Palestinian Village Histories: Geographies of the Displaced. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. ISBN 978-0-8047-7312-6.
- Department of Statistics (1945). Village Statistics, April, 1945. Government of Palestine.
- Hadawi, S. (1970). Village Statistics of 1945: A Classification of Land and Area ownership in Palestine. Palestine Liberation Organization Research Centre.
- Hartmann, M. (1883). "Die Ortschaftenliste des Liwa Jerusalem in dem türkischen Staatskalender für Syrien auf das Jahr 1288 der Flucht (1871)". Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins. 6: 102–149.
- Khalidi, W. (1992). All That Remains: The Palestinian Villages Occupied and Depopulated by Israel in 1948. Washington D.C.: Institute for Palestine Studies. ISBN 0-88728-224-5.
- Mills, E., ed. (1932). Census of Palestine 1931. Population of Villages, Towns and Administrative Areas. Jerusalem: Government of Palestine.
- Morris, B. (2004). The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-00967-6. (pp. 233, 235, 237, 345, 371, 376, 380, 407)
- Palmer, E. H. (1881). The Survey of Western Palestine: Arabic and English Name Lists Collected During the Survey by Lieutenants Conder and Kitchener, R. E. Transliterated and Explained by E.H. Palmer. Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Petersen, Andrew (2002). A Gazetteer of Buildings in Muslim Palestine (British Academy Monographs in Archaeology). Vol. 1. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-727011-0.
- Pringle, D. (1997). Secular buildings in the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem: an archaeological Gazetter. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521460101.
- al-Qawuqji, F. (1972): Memoirs of al-Qawuqji, Fauziin Journal of Palestine Studies
- "Memoirs, 1948, Part I" in 1, no. 4 (Sum. 72): 27-58., dpf-file, downloadable
- , dpf-file, downloadable
- Robinson, E.; Smith, E. (1841). Biblical Researches in Palestine, Mount Sinai and Arabia Petraea: A Journal of Travels in the year 1838. Vol. 3. Boston: Crocker & Brewster.
- Salih, ‘Uthman Muhammad (1988). Bayt Mahsir [Bayt Mahsir]. Al-Baq‘a, Jordan: n.p.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Schick, C. (1896). "Zur Einwohnerzahl des Bezirks Jerusalem". Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins. 19: 120–127.
- Socin, A. (1879). "Alphabetisches Verzeichniss von Ortschaften des Paschalik Jerusalem". Zeitschrift des Deutschen Palästina-Vereins. 2: 135–163.
External links[edit]
- Welcome To Bayt Mahsir
- Bayt Mahsir, Zochrot
- Survey of Western Palestine, Map 17: IAA, Wikimedia commons
- Mosque of Sheikh Ahmad el-‘Ajami
- Bayt Mahsir, from the Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center