Liber Secretorum Fidelium Crucis

The Liber Secretorum Fidelium Crucis (literally "Book of the Secrets of the Faithful of the Cross") is a Latin work by Marino Sanuto the Elder. It is one of the "recovery of the Holy Land" treatises intended to inspire a revival of the Crusades. It has also been named as Historia Hierosolymitana and Liber de expeditione Terrae Sanctae, and Opus Terrae Sanctae, the last being perhaps the proper title of the whole treatise as completed in three parts or "books".[1]
It was begun in March 1306, and finished (in its earliest form) in January 1307, when it was offered to Pope Clement V as a manual for true Crusaders who desired the reconquest of the Holy Land. To this original Liber Secretorum Sanuto added largely; two other "books" were composed between December 1312 and September 1321, when the entire work was presented by the author to Pope John XXII, together with a map of the world, a map of Palestine, a chart of the Mediterranean, Black Sea and west European coasts, and plans of Jerusalem, Antioch and Acre. A copy was also offered to the king of France, to whom Sanuto desired to commit the military and political leadership of the new crusade.[1]
This work has much to say of trade and trade-routes as well as of political and other history; and through its accompanying maps and plans it occupies an important place in the development of cartography.
Proposals[edit]
The crusading plans of the Secreta are double: first, Egypt and the Muslim world on the side towards Europe (Syria, Asia Minor, the Barbary States (North Africa), Granada, etc.) are to be ruined by the absolute stoppage of all Christian trade with the same. By such an interdict Sanuto hopes that Egypt, dependent on its European and other imports of metals, provisions, weapons, timber, pitch and slaves, would be fatally weakened, and the way thus prepared for the second part of the campaign the armed attack of the crusading fleet and army on the Nile delta. With the aid of the Mongol Tatars of Asia, natural allies of western Christendom, and of the Nubian Christian kingdom of Makuria, the conquest of the Delta and of all Egypt was to be followed by that of Palestine, invaded and held from Egypt. Sanuto deprecates any other route for the crusade, and unfolds his plan of campaign, his bases of supply, his sources for the supply of good seamen, with great detail. Not only Mediterranean seaports, but the lakes of North Italy and central Europe, and the Hanseatic ports, are enumerated as nurseries of crusading mariners and marine skill. Finally, after the conquest of Egypt, Marino designs the establishment of a Christian fleet in the Indian Ocean to dominate and subjugate its coasts and islands. He also gives a sketch of the trade-routes crossing Persia and Egypt, as well as of the course of Indian trade from Coromandel and Gujarat to Hormuz and the Persian Gulf, and to Aden and the Nile.
Maps[edit]
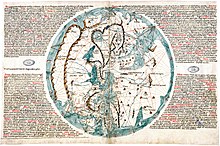
The maps and plans which illustrate the Secreta are probably (in the main, at least) the work of the great portolan chart draughtsman Pietro Vesconte: practically the whole of this map-work corresponds with what Vesconte has left under his own name; much of it is indistinguishable. Among the plans that of Acre is of peculiar interest, being the most complete representation known of the great crusading fortress on the eve of its destruction, with the quarters of all its contingents of defenders (Templars, etc.) indicated. The chart of the Mediterranean and Euxine and of the Atlantic coasts of Europe is composed of five map-sheets, which together form a good example of the earliest scientific design or portolano; in the world-map a portolano of the Mediterranean world Is combined with work of pre-portolan type in remoter regions. Here the shore-lines of the countries well known to Italian mariners, from Flanders to Azov, are well laid down; the Caspian and the north German and Scandinavian coasts appear with an evident, though far slighter, relation to practical knowledge; and some idea is shown of the great continental rivers of the north, such as the Don, Volga, Vistula, Oxus and Syr Daria. Africa, away from the Mediterranean, is conventional, with its south-east projected, after the manner of Idrisi, so as to face Indian Asia, and with a western Nile traversing the continent to the Atlantic. Chinese and Indian Asia show little trace of the new knowledge which had been imparted by European pioneers from the Polos' time, and which appears so strikingly in the Catalan Atlas of 1375. Sanuto's Palestine map is remarkable for its space-defining network of lines, which roughly answer to a kind of scheme of latitude and longitude, though properly speaking they are not scientific at all. Of the Secreta, twenty-three MSS. exist, of which the chief are: Florence, Biblioteca Riccardiana, No. 237, 162 fols. (Secreta and Letters), with maps and plans on fols. 141, v.-144, r.; (2) London, British Museum, Addt. MSS., 27,376, 178 fols. with maps, &c. on fols. 18o, v.-190, r.; (3) Paris, National Library, MSS. Lat. 4939, with maps, &c. on fols. 9, r.-I I, r. 27, 98–99. All these are of the 14th century.
Versions[edit]
A number of original manuscripts are known. Important manuscripts including maps include:[2]
- Rome: Vatican Library lat. 2972
- Rome: Bibl. Regin. 548
- London: British Library 27376
- Paris: Bibliothèque nationale de France 4939
- Brussels: Royal Library of Belgium 9404
- Brussels: Royal Library of Belgium 9347
- Florence: Biblioteca Riccardiana 237
- Florence: Laurentian Library XXi 23
- Naples: Biblioteca Nazionale Vittorio Emanuele III 35
Other manuscripts include:
The Secreta has only once been printed entire, by Bongars, in Gesta Dei per Francos, vol. ii. pp. 1–288 (Hanover, 1611). This was reprinted by the University of Toronto Press in 1972 with an English foreword by Joshua Prawer.
- First printed version (1611): Sanuto, Marino detto Torsello sen (1611). Liber Secretorum Fidelium Crucis Super Terrae Sanctae Recuperatione Et Conservatione quo Et Terrae Sanctae Historia ab Origine. Et Ejusdem vicinarumque Provinciarum Geographica descriptio continetur: 2. Aubrius.
It was translated by Peter Lock and first published in 2011:
- Lock, Peter (6 May 2016). Marino Sanudo Torsello, The Book of the Secrets of the Faithful of the Cross: Liber Secretorum Fidelium Crucis. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-317-10059-1.
- Marino Sanudo Torsello, The Book of the Secrets of the Faithful of the Cross: Liber Secretorum Fidelium Crucis, trans by Peter Lock, Crusade Texts in Translation (Farnham: Ashgate, 2011)
References[edit]
- ^ a b Leopold, Antony (1 January 2000). How to Recover the Holy Land: The Crusade Proposals of the Late Thirteenth and Early Fourteenth Centuries. Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-0120-3.
- ^ K. Kretschmer, Marino Sanudo der Ältere und die Karten des Petrus Vesconte, Z. Ges. Erdk. Berlin 1891, page 355
