Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone bisoxalate
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]bis([1,4]dioxine)hexone | |
| Other names
Benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']bis-p-dioxin-2,3,5,7,8,10-hexone (8CI)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10O10 | |
| Molar mass | 280.00 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
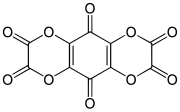
Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone bisoxalate is a chemical compound, an oxide of carbon with formula C
10O
10. Its molecule consists of a 1,4-benzoquinone core with the four hydrogen atoms replaced by two oxalate groups. It can be seen as a fourfold ester of tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone and oxalic acid.
The compound was first described by H. S. Verter, H. Porter, and R. Dominic in 1968. It was obtained by reacting tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone with oxalyl chloride in tetrahydrofuran. It is a yellow solid that can be crystallized as a tetrahydrofuran solvate, but could not be prepared in pure form.[1]
See also[edit]
- Tetrahydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone biscarbonate
- Hexahydroxybenzene trisoxalate
- Hexahydroxybenzene triscarbonate
References[edit]
- ^ H. S. Verter, H. Porter, and R. Dominic (Verter, Porter and Dominic, 1968), A new carbon oxide: synthesis of tetrahydroxybenzoquinone bisoxalate. Chemical Communications, p. 973b–974. doi:10.1039/C1968000973b
