Nicene Christianity

Nicene Christianity, or Traditional Christianity, includes those Christian denominations that adhere to the teaching of the Nicene Creed,[1] which was formulated[2] at the First Council of Nicaea in AD 325 and amended at the First Council of Constantinople in AD 381.[3]
History[edit]
At the time of the First Council of Nicaea, the main rival of Nicene Christian doctrine was that of Arianism, which became eclipsed during the 7th century AD with the conversion of the Gothic kingdoms to Nicene Christianity. The main points of dissent between the two centered on Christology, or the nature of Jesus' divinity. Nicene Christianity regards Jesus as divine and co-eternal with God the Father, while Arianism treats him as the first among created beings and inferior to God the Father. Various other non-Nicene doctrines and beliefs have existed since the early medieval period, all of which have been considered heresies.[2]
Religious historians and scholars often define Nicene Christianity as being the first incarnation of the state church of the Roman Empire that was officially endorsed by the Roman Emperors from 381. According to this definition, the Nicene Church ceased to exist following the Council of Chalcedon in 451, which was convened to address Christological disagreements on the human and divine natures of Christ, concluding that Christ had two separate natures. Following the council, the Roman Empire established Chalcedonian Christianity as its official state religion; those churches which held that Christ was of a single nature were excommunicated by Rome and became the Oriental Orthodox Churches.
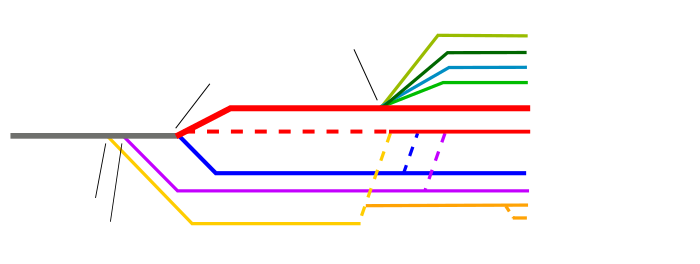
- (Not shown are ante-Nicene, nontrinitarian, and restorationist denominations.)
Today, examples of non-Nicene Christian denominations encompass both Protestant and non-Protestant non-trinitarian groups. Examples of these groups include the majority of the Latter Day Saint movement (with the exception of the Nicene Mormon group known as the Community of Christ [formerly known as the Reorganized Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints]), the Unitarian Church of Transylvania, Oneness Pentecostals, and others.[citation needed]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ World Encyclopaedia of Interfaith Studies: World religions. Jnanada Prakashan. 2009. ISBN 978-81-7139-280-3.
In the most common sense, "mainstream" refers to Nicene Christianity, or rather the traditions which continue to claim adherence to the Nicene Creed.
- ^ a b "Nicene Creed". Encyclopedia Britannica. 3 January 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Siddhartha 2009, p. 733.
Sources[edit]
- Siddhartha, Anand (2009). World Encyclopaedia of Interfaith Studies: World religions. Vol. 3. New Delhi: Jnanada Prakashan. ISBN 978-81-7139-280-3.
- Spinks, Bryan D. (2013). Do this in Remembrance of Me: The Eucharist from the Early Church to the Present Day. SCM Press. ISBN 978-0-334-04376-8.
